Cross-Border E-Commerce for Foreign Companies Without Japanese Operations
Cross-border e-commerce business, where foreign companies sell products and services directly to Japanese consumers through their own websites without establishing operations in Japan, represents a rapidly expanding market opportunity. The cross-border e-commerce market size is predicted to grow rapidly from $785 billion USD in 2021 to $7.938 trillion USD by 2030. Notably, purchases of Japanese products from China exceed 2 trillion yen, indicating substantial business opportunities.
The Japanese market is a mature market with high purchasing power, showing particularly strong demand for product categories such as cosmetics and beauty products, children’s products and diapers, luxury watches and branded goods, anime and game-related merchandise, and clothing and accessories. However, success requires compliance with Japan-specific legal requirements, understanding of business customs, and a staged, systematic approach.
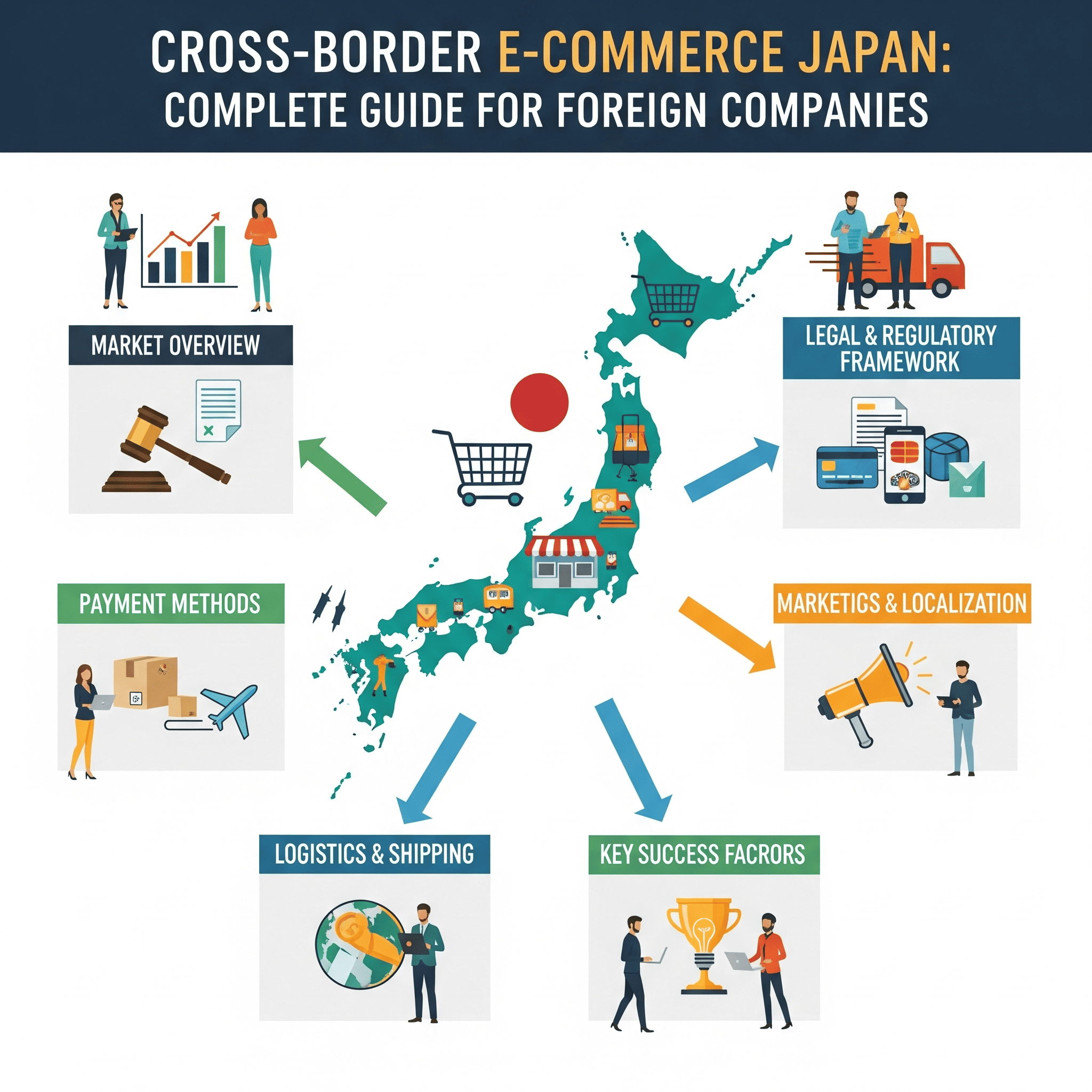
This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap for foreign companies to succeed in cross-border e-commerce business in Japan through six staged phases. We offer practical content covering legal compliance, technical implementation, and marketing strategies, assuming a 12-18 month business launch period.
Basic Concepts of Cross-Border E-Commerce and Importance of Japanese Market Entry
Cross-border e-commerce refers to a form of electronic commerce where foreign companies sell products or services to consumers in other countries via the internet while maintaining operations in their home country. This is an efficient business model that allows access to the Japanese market while avoiding large initial investments and complex corporate establishment procedures associated with establishing physical operations.
The appeal of the Japanese market lies in its maturity and consumers’ high purchasing power. Japanese consumers have strong demand for high-quality products and services, showing particular interest in excellent overseas products. Additionally, high internet penetration rates and the establishment of online shopping create a market environment suitable for cross-border e-commerce.
However, entering the Japanese market also presents unique challenges. Understanding and appropriately responding to strict legal requirements, expectations for high quality standards, and unique business customs and cultural backgrounds are prerequisites for success. By overcoming these challenges, it becomes possible to secure long-term, stable revenue sources.
Three Essential Legal Requirements for Cross-Border E-Commerce in Japan
The main legal requirements that foreign companies must comply with when conducting cross-border e-commerce business in Japan are consumption tax law, specified commercial transactions law, and personal information protection law. Appropriate response to these legal requirements forms the foundation for ensuring business continuity and reliability.
Regarding consumption tax, domestic or international transactions are determined based on the location of goods, and consumption tax is imposed when foreign companies transfer assets in Japan. Particularly important is that when annual taxable sales exceed 10 million yen, the company becomes a taxable business operator and must file a tax administrator notification. Tax administrators are typically outsourced to tax accountants within Japan.
Article 11 of the Specified Commercial Transactions Law mandates the posting of statutory disclosure items on e-commerce sites. Specifically, business operator’s name (title), address, and phone number; product sales prices and shipping fees; payment methods and payment timing; product delivery timing; returns, exchanges, and cancellations; and responsible person’s name must be accurately described in Japanese on a “Legal Disclosure Based on Specified Commercial Transactions Law” page and displayed in locations easily recognizable by consumers.
Compliance with the Personal Information Protection Law requires specification, notification, and publication of usage purposes, with special provisions for providing personal data to foreign countries. Implementation of appropriate safety management measures and establishment of systems to respond to individual disclosure requests are required. Privacy policies must be created in Japanese with specific and easily understandable usage purposes.

Six Phases to Success: Staged Business Development Approach
Success in cross-border e-commerce business requires a systematic, staged approach. By sequentially executing the following six phases, you can minimize risks while reliably launching and growing your business.
Phase 1’s preliminary research and planning (2-3 months) involves market research, target customer identification, competitor analysis, product selection, and confirmation of import/export regulations. This stage is the most important period forming the foundation of the business, involving detailed analysis of Japanese market characteristics and compatibility with your products.
Phase 2’s legal compliance system establishment (3-4 months) involves establishing response systems for consumption tax, specified commercial transactions law, and personal information protection law. Tax administrator selection, legal disclosure preparation, privacy policy creation, and complete elimination of legal risks are conducted.
Phase 3’s website and system construction (4-6 months) involves Japanese-compatible e-commerce site development, payment system construction, and logistics system establishment. Rather than simple translation, localization including Japanese cultural considerations is implemented, with UI/UX designed according to Japanese business customs.
Phase 4’s marketing and customer acquisition preparation (2-3 months) involves digital marketing strategy formulation and email marketing system construction. Preparation for Japan-specific SEO measures, social media marketing, and influencer collaborations proceeds.
Phase 5’s operation launch and initial response (1-2 months) begins with soft launch test sales and customer support system operation. Starting with small-scale sales to identify issues and make final adjustments toward full-scale operation.
Phase 6’s full-scale operation and expansion (continuous implementation) involves sales expansion measure implementation and continuous improvement. Data analysis-based strategy reviews, product lineup expansion, customer satisfaction improvements, and other measures are continuously implemented to accelerate business growth.
Technical Requirements and Implementation Points for E-Commerce Site Construction
Construction of cross-border e-commerce sites targeting Japan requires technical requirements and Japan-specific considerations. Successful e-commerce sites must achieve high levels in three elements: functionality, usability, and legal compliance.
For multilingual support and localization, it’s important that Japanese site construction involves genuine localization including Japanese cultural considerations, not mere translation. Colors, text placement, and navigation composition should be designed according to Japanese preferences and customs, providing intuitive and user-friendly interfaces.
For payment systems, supporting popular payment methods in Japan directly affects customer satisfaction. In addition to credit card payments, providing multiple options such as convenience store payments, bank transfers, and mobile payments (PayPay, LINE Pay, etc.) is important. Prices should be clearly displayed in yen, and security measures including SSL and 3D Secure are essential requirements.
Implementation of legal compliance features requires incorporating automatic display functions for items required by the Specified Commercial Transactions Law, mandatory displays on final confirmation screens, and clarification of return and exchange flows. Additionally, consent acquisition functions corresponding to the Personal Information Protection Law, data management and deletion functions, and security measures must be technically implemented to construct systems that automatically maintain legal compliance.
Logistics System and Delivery Optimization Strategy
An efficient and reliable logistics system is a crucial element for cross-border e-commerce business success. Since Japanese consumers have high expectations for delivery speed and accuracy, constructing appropriate logistics strategies directly affects customer satisfaction and business continuity.
Basic international shipping options should include delivery methods such as EMS (Express Mail Service) and international courier services, with shipping costs and delivery times clearly displayed in advance. Multiple delivery options should be prepared, allowing selection based on customer needs and budgets to serve a wide range of customer segments.
Collaboration with local delivery companies enables faster and more reliable delivery. Partnering with domestic Japanese delivery companies allows for shortened delivery times, and utilizing local warehouse services can also reduce delivery costs. Implementing delivery tracking systems to provide environments where customers can check package status in real-time is also important.
Return and exchange support requires clear policies and rapid response systems that meet Japanese consumers’ high quality expectations. Detailed explanation of return and exchange conditions, procedures, and cost responsibilities, and establishing environments where customers can purchase with confidence forms the foundation for long-term customer relationship building.
Risk Management and Continuous Compliance Maintenance Systems
Cross-border e-commerce business requires responses to various risks including legal risks, operational risks, and market risks. By appropriately managing these risks and continuously maintaining compliance, stable business operations can be realized.
Legal risk response centers on consumer dispute handling, tax risk management, and continuous response to legal revisions. By implementing preventive measures such as preventing misunderstandings through appropriate displays, rapid complaint responses, and preparation for legal disputes, major troubles can be prevented. Through continuous collaboration with legal and tax experts, it’s important to continue adapting to changing legal environments.
Operational risk management requires pricing strategies for foreign exchange fluctuation risks, understanding Japanese business customs and appropriate communication for cultural risks, and continuous market analysis and strategy reviews. By constructing systems that can flexibly respond to market environment changes, long-term competitiveness can be maintained.
Through continuous collaboration with experts, you can continue responding to the latest trends in each field. Through regular information exchange and cooperation systems with experts in legal, tax, marketing, and translation/localization fields, constructing systems that adapt to changing environments and continuously support business growth is key to success.
Four Basic Principles for Achieving Success
To achieve sustainable success in cross-border e-commerce business, it’s essential to thoroughly practice four basic principles. These principles are practical success factors formulated based on Japanese market characteristics and consumer expectations.
The quality-first principle recognizes that Japanese consumers have particularly high quality expectations worldwide, making it important not to compromise on product and service quality. By aiming to provide products and services comparable to Japanese product quality and design levels, and engaging in continuous quality improvement, differentiation from competitors can be realized.
The reliability assurance principle prioritizes gaining customer trust through complete legal requirement compliance, transparent transactions, and rapid, courteous customer service. Trust becomes the foundation of long-term customer relationships and becomes important assets supporting business growth through word-of-mouth and repeat purchases.
The localization investment principle actively invests in Japan-specific measures such as Japanese language information provision, Japanese payment method support, and consideration for local business customs. This investment enables differentiation from competitors and provides better purchasing experiences for Japanese consumers, establishing competitive advantages in the market.
The long-term perspective principle emphasizes long-term success over short-term profits, developing strategies considering the continuous growth of the cross-border e-commerce market. Through continuous improvement and innovation, and investment in brand building, sustainable business models can be constructed to solidify market positions.
Conclusion: A Definitive Path to Success
Foreign companies can successfully achieve cross-border e-commerce business without Japanese operations through appropriate preparation and staged approaches. Sustainable success in the Japanese market can be realized through systematic development via six phases, complete legal requirement compliance, appropriate technical requirement implementation, efficient logistics systems, continuous risk management, and practice of four basic principles.
By following this roadmap and proceeding with staged preparation, you can minimize risks while reliably launching and growing your business. However, since requirements may differ depending on specific products or services, consulting experts at each stage is also an important success factor.
Japan’s cross-border e-commerce market is an attractive market with continuous growth expected in the future. Through appropriate preparation and continuous improvement, even foreign companies can achieve great success in the Japanese market. Use this guide to take the first step toward success in Japanese cross-border e-commerce business.