What is a resident?
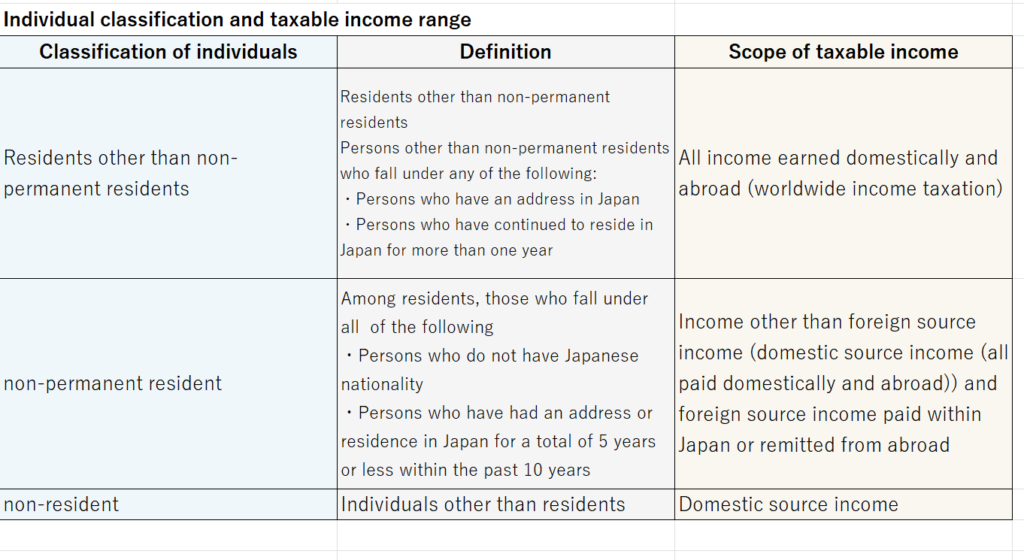
According to the Income Tax Act, a “resident” is defined as an individual who has an address in Japan or an individual who has continued to reside in Japan for one year or more. Residents are liable for Japanese income tax on their worldwide income.
What is a non-permanent resident?
Non-permanent residents are residents who do not have Japanese nationality and have had an address or residence in Japan for a total of 5 years or less within the past 10 years. defined as “permanent resident”. The scope of taxable income for non-permanent residents is limited to income other than foreign source income (domestic source income that is paid regardless of whether it is abroad or domestic) and the portion of foreign source income that is paid domestically or remitted domestically.
If a resident has Japanese nationality and has an address or residence in Japan for one year or more, he or she is considered a resident, regardless of the period of residence or residence.
What is a non-resident?
A non-resident is defined as an individual who does not have an address or residence in Japan. Non-residents are liable for Japanese income tax only on domestic source income. The scope of taxable income for non-residents is limited to domestic source income, and if the income is not attributable to a permanent establishment, a separate taxation method with source is used, in which the taxation relationship is completed only with withholding tax. It has become.
Scope of taxable income
Scope of resident taxable income
Residents are taxed on their worldwide income.
Scope of taxable income for non-permanent residents
Non-permanent residents are subject to tax on income other than income generated abroad (foreign source income) as stipulated in the Income Tax Act, and on foreign source income paid or remitted within Japan.
Scope of taxable income for non-residents
A non-resident is an individual who does not have an address or residence in Japan. Non-residents are liable for Japanese income tax only on domestic source income. Specifically, the following income is considered domestic source income.
- Income from the transfer of real estate in Japan
- Income from the transfer of domestic mining rights, patent rights, etc.
- Income generated from doing business in Japan
- Income generated domestically from the provision of human services, writing, acting, and other human activities or labor is only applicable if the income is earned domestically, with the exception of special provisions for determining domestic source income such as business administration. , income arising from this
- Income from lending real estate in Japan
- Income from lending domestic movable property or intangible property that does not fall under special provisions
- Income paid by a Japanese resident, domestic corporation, or permanent establishment to a non-resident, foreign person, or foreign corporation that is deemed to be a domestic source under a tax treaty.
- Dividends of surplus, distribution of profits, distribution of surplus received from domestic corporations
Summary
As mentioned above, the range of income subject to tax varies greatly depending on the definition of resident and non-resident. Residents are taxed on their worldwide income, while non-residents are taxed only on Japan domestic source income. This is based on the two concepts of taxation in the country of residence and taxation in the source country under Japanese tax law. Country of residence taxation is the concept of taxing a resident’s worldwide income, and source country taxation is the concept of taxing that income in the country where the income originates.
While we strive for accuracy in the content of this website, it is based on laws and regulations as of January 1, 2025 (Reiwa 7) and represents the author’s analysis. We make no warranty regarding its accuracy, completeness, suitability for any purpose, or any other aspect. Furthermore, we do not track legal amendments after this date. We accept no liability whatsoever for any damages arising from actions taken or not taken based on this website or the materials contained herein.